Docker
I am going to show you how to install docker in Linux platform, the operating system I am using here is CentOS 7 64 bit architecture. In my previous tutorial I had shown how to install docker on Windows 7 operating system.
Docker is a container, more like a virtual machine, portable, resource friendly and dependent on the host operating system. Using docker makes an application simple and easy to run in a container.
Why do you need docker?
It allows developers to create a portable application that could be run on every machine. Instead of delivering jar, war, ear or other type of artifacts for your applications, you deliver an image and someone else who wants to deploy your application, basically deploys the image on a machine with pre-installed docker. With docker installed you don’t have dependency of setting up the environments.
Prerequisites
CentOS 7 64 bit droplet, Non-root user with sudo privilege
Install Docker
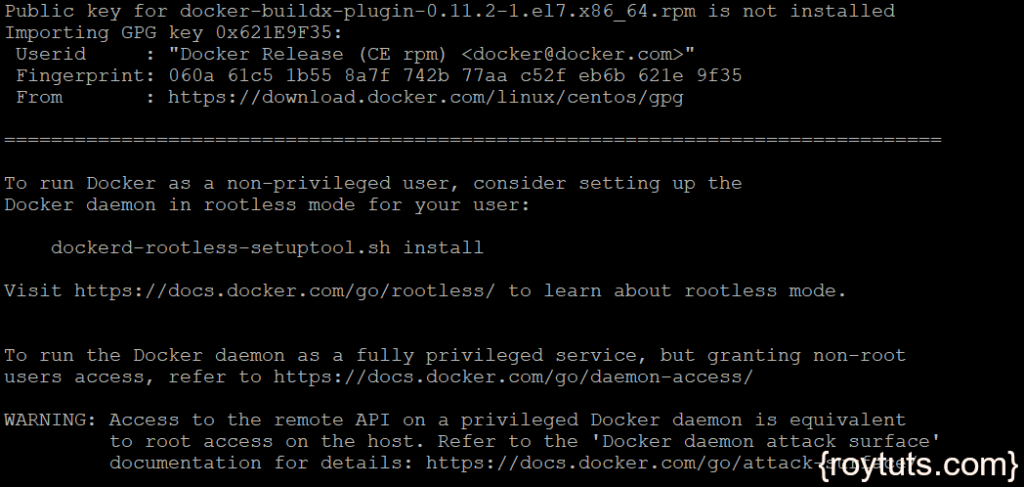
before you install docker on your system, make sure you get the latest docker package from the official docker repository, because the available docker package in your CentOS droplet may not be the latest version. To get the latest version execute the following commands. The first command will update your package database and the second command will download the latest version from docker official repository and install it.
$ sudo yum check-update
$ curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com/ | shCommand arguments -fsSL has the following meaning:
- f: Fail silently (no output at all) on server errors.
- s: Silent or quiet mode. Don’t show progress meter or error messages.
- S: When used with
-sit makes curl show an error message if it fails. - L: (HTTP/HTTPS) If the server reports that the requested page has moved to a different location (indicated with a Location: header and a 3XX response code), this option will make curl redo the request on the new place.
| sh with curl command starts curl and sh at the same time, connecting the output of curl to the input of sh. curl will carry out with the download as fast as sh can run the script.
Once the installation has been completed, you will see similar screen as shown in the following image:
Installation complete, now you can start the docker using the following command:
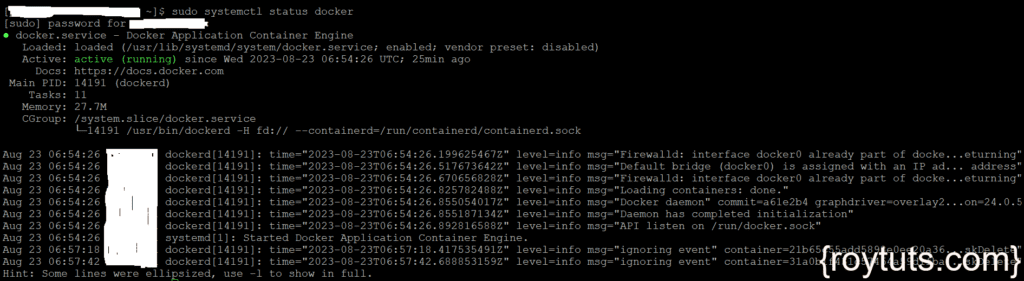
$ sudo systemctl start dockerNow you can check the status of the docker whether it is running or not:
$ sudo systemctl status dockerThe output should be similar to the below image:
Finally, make sure it starts on every server reboot by following command:
$ sudo systemctl enable docker
Docker Commands
You can view all available sub-commands using the command $ docker. It will list the following commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
deploy Deploy a new stack or update an existing stack
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
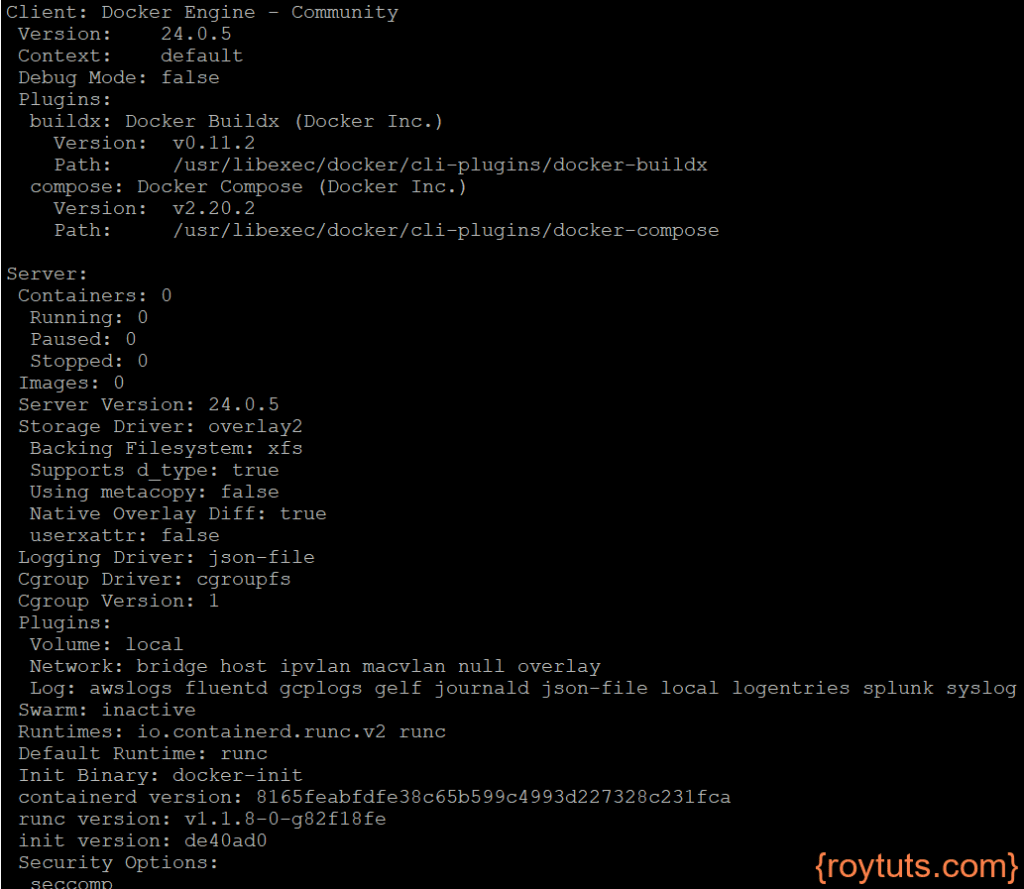
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.You may also view system wide information using the command $ docker info.
At this point you might get permission denied or access denied error if you have not added the user into docker group after the installation.
Perform the following steps in order to add the user.
- Execute command
$ sudo usermod -aG docker <user name> - Reflect the change using command
$ newgrp docker - Restart docker
$ sudo systemctl restart docker
Now you can re-execute the command $ docker info to view system wide information.
Docker Images
Docker containers run from docker images and these images are pulled from docker hub, a registry managed by docker. Anyone can build and host docker images into docker hub. Most of the applications that you need to run docker containers have docker images in docker hub.
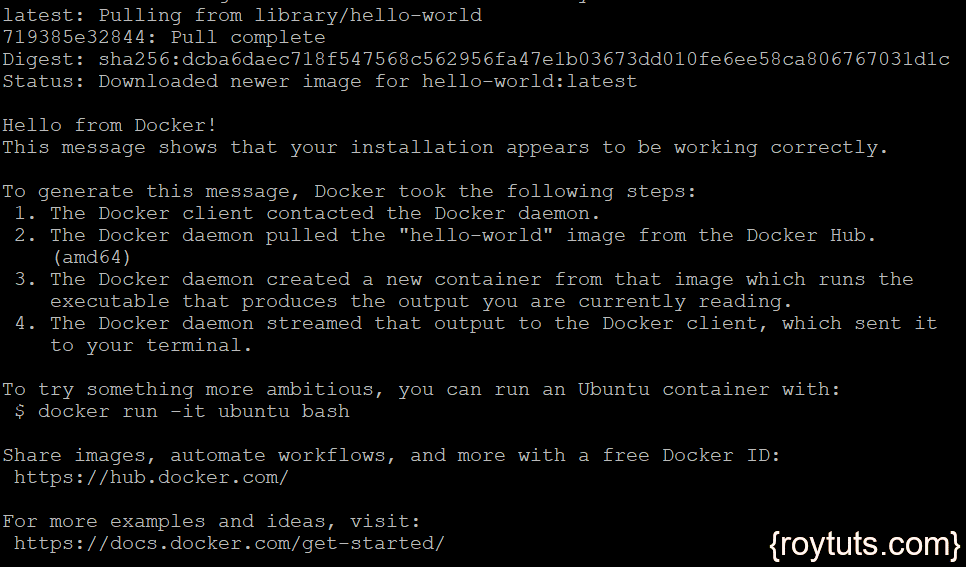
You can check whether docker hub is accessible or not by using the following command:
$ docker run hello-worldThe following output shows docker is working properly:
To list docker images on your system you can use the following command:
$ docker imagesIn the following image you can see that the only image I had puleed from docker hub in the previous step:
You can also check which docker containers are currently running by executing the command $ docker ps.
That’s all about installing docker in CentsOS 7 operating system.