CSV To MySQL
This tutorial will show you how to read a csv file data and write to MySQL database. I will make some modification to the csv data and insert into MySQL database. You can read the tutorial Spring Batch to read what is Spring Batch and what are the usages of Spring Batch.
Prerequisites
Java 8/11/19, Maven 3.8.5, Spring Boot 2.6.7/3.1.2
I’ll build a service that imports data from a CSV file, transforms it with custom code, and stores the final results in MySQL Database.
Related Posts:
Project Setup
Create a maven based project in your favorite IDE or tool and you will see the required project structure gets created.
Spring Boot 3.x
For Spring Boot 3.x version use the following pom.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.roytuts</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-csv-to-mysql</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>19</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>19</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.1.2</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-oxm</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.xml.bind-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish.jaxb</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-runtime</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.31</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Spring Boot 2.x
Use the following pom.xml file for Spring Boot 2 version.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.roytuts</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-csv-to-mysql</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.7</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-oxm</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.xml.bind-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish.jaxb</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-runtime</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>MySQL Table
The following person table is created under roytuts database.
CREATE TABLE `person` (
`id` int unsigned COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`firstName` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`lastName` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;VO Class
Create a model class Person.java which will represent a row of data for inputs and outputs.
Please note that for Spring Boot 2.x and Spring Boot 3.x will have different import statements for the XML related things.
public class Person {
private int id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
@XmlAttribute(name = "id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + "]";
}
}ItemProcessor Class
FielSetMapper is no longer required because I will store data into database, so create an intermediate processor. A common paradigm in batch processing is to ingest data, transform it, and then pipe it out somewhere else. Here I write a simple transformer that converts the initial characters of the names to uppercase.
public class PersonItemProcessor implements ItemProcessor<Person, Person> {
@Override
public Person process(Person person) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Processing: " + person);
final String initCapFirstName = person.getFirstName().substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ person.getFirstName().substring(1);
final String initCapLastName = person.getLastName().substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ person.getLastName().substring(1);
Person transformedPerson = new Person();
transformedPerson.setId(person.getId());
transformedPerson.setFirstName(initCapFirstName);
transformedPerson.setLastName(initCapLastName);
return transformedPerson;
}
}Input CSV File
Create below CSV file person.csv under src/main/resources directory.
1000,soumitra,roy
1001,souvik,sanyal
1002,arup,chatterjee
1003,suman,mukherjee
1004,debina,guha
1005,liton,sarkar
1006,debabrata,poddarConfiguration Class
I have created this Spring Configuration class to define several beans for Spring Batch processing.
I have defined beans, such as, ItemProcessor, TransactionManager, JobRepository, DataSource, JobLauncher, Step, Job etc. for our Spring Batch processing.
For Spring Boot version 3.x use the following configuration class.
In spring boot 3.x you don’t need to use @EnableBatchProcessing annotation on the configuration class.
The RunIdIncrementer() has not been used for getting the unique run id, instead setIncrementerFactory() method has been used while creating the JobRepository instance. Otherwise you will get the following exception:
Failed to instantiate [org.springframework.batch.core.repository.JobRepository]: Factory method 'jobRepository' threw exception with message: Cannot invoke "org.springframework.batch.item.database.support.DataFieldMaxValueIncrementerFactory.getIncrementer(String, String)" because "this.incrementerFactory" is nullThe JobBuilderFactory and StepBuilderFactory have been removed and you can now use JobBuilder and StepBuilder to create respective instances with JobRepository and PlatformTransactionManager instances.
@Configuration
public class SpringBatchConfig {
@Bean
@Scope(value = BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public Person person() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@Scope(value = BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public ItemProcessor<Person, Person> itemProcessor() {
return new PersonItemProcessor();
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/roytuts");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
ResourceDatabasePopulator databasePopulator = new ResourceDatabasePopulator();
databasePopulator.addScript(new ClassPathResource("org/springframework/batch/core/schema-drop-mysql.sql"));
databasePopulator.addScript(new ClassPathResource("org/springframework/batch/core/schema-mysql.sql"));
DatabasePopulatorUtils.execute(databasePopulator, dataSource);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public ResourcelessTransactionManager txManager() {
return new ResourcelessTransactionManager();
}
@Bean
public JobRepository jbRepository(DataSource dataSource, ResourcelessTransactionManager transactionManager)
throws Exception {
JobRepositoryFactoryBean factory = new JobRepositoryFactoryBean();
factory.setDatabaseType(DatabaseType.MYSQL.getProductName());
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setTransactionManager(transactionManager);
factory.setIncrementerFactory(new DefaultDataFieldMaxValueIncrementerFactory(dataSource) {
@Override
public DataFieldMaxValueIncrementer getIncrementer(String incrementerType, String incrementerName) {
return new SqlServerSequenceMaxValueIncrementer(dataSource, incrementerName);
}
});
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
@Bean
public JobLauncher jbLauncher(JobRepository jobRepository) {
TaskExecutorJobLauncher jobLauncher = new TaskExecutorJobLauncher();
jobLauncher.setJobRepository(jobRepository);
return jobLauncher;
}
@Bean
public BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<Person> beanWrapperFieldSetMapper() {
BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<Person> fieldSetMapper = new BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<>();
fieldSetMapper.setPrototypeBeanName("person");
return fieldSetMapper;
}
@Bean
public FlatFileItemReader<Person> fileItemReader(BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<Person> beanWrapperFieldSetMapper) {
FlatFileItemReader<Person> fileItemReader = new FlatFileItemReader<>();
fileItemReader.setResource(new ClassPathResource("person.csv"));
DelimitedLineTokenizer delimitedLineTokenizer = new DelimitedLineTokenizer();
delimitedLineTokenizer.setNames("id", "firstName", "lastName");
DefaultLineMapper<Person> defaultLineMapper = new DefaultLineMapper<>();
defaultLineMapper.setLineTokenizer(delimitedLineTokenizer);
defaultLineMapper.setFieldSetMapper(beanWrapperFieldSetMapper);
fileItemReader.setLineMapper(defaultLineMapper);
return fileItemReader;
}
@Bean
public JdbcBatchItemWriter<Person> jdbcBatchItemWriter(DataSource dataSource,
BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<Person> sqlParameterSourceProvider) {
JdbcBatchItemWriter<Person> jdbcBatchItemWriter = new JdbcBatchItemWriter<>();
jdbcBatchItemWriter.setDataSource(dataSource);
jdbcBatchItemWriter.setItemSqlParameterSourceProvider(sqlParameterSourceProvider);
jdbcBatchItemWriter.setSql("insert into person(id,firstName,lastName) values (:id, :firstName, :lastName)");
return jdbcBatchItemWriter;
}
@Bean
public BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<Person> beanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider() {
return new BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<>();
}
@Bean
public Job jobCsvMysql(JobRepository jobRepository, Step step) {
return new JobBuilder("jobCsvMysql", jobRepository).flow(step).end().build();
// return new JobBuilder("jobCsvMysql", jobRepository).start(step).build();
}
@Bean
public Step step1(JobRepository jobRepository, ResourcelessTransactionManager transactionManager,
ItemReader<Person> reader, ItemWriter<Person> writer, ItemProcessor<Person, Person> processor) {
return new StepBuilder("step1", jobRepository).<Person, Person>chunk(2, transactionManager).reader(reader)
.processor(processor).writer(writer).build();
}
}For Spring Boot version 2.x use the following configuration class.
@Configuration
@EnableBatchProcessing
public class SpringBatchConfig {
@Bean
@Scope(value = BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public Person person() {
return new Person();
}
@Bean
@Scope(value = BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE)
public ItemProcessor<Person, Person> itemProcessor() {
return new PersonItemProcessor();
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/roytuts");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("");
ResourceDatabasePopulator databasePopulator = new ResourceDatabasePopulator();
databasePopulator.addScript(new ClassPathResource("org/springframework/batch/core/schema-drop-mysql.sql"));
databasePopulator.addScript(new ClassPathResource("org/springframework/batch/core/schema-mysql.sql"));
DatabasePopulatorUtils.execute(databasePopulator, dataSource);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public ResourcelessTransactionManager txManager() {
return new ResourcelessTransactionManager();
}
@Bean
public JobRepository jbRepository(DataSource dataSource, ResourcelessTransactionManager transactionManager)
throws Exception {
JobRepositoryFactoryBean factory = new JobRepositoryFactoryBean();
factory.setDatabaseType(DatabaseType.MYSQL.getProductName());
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setTransactionManager(transactionManager);
return factory.getObject();
}
@Bean
public JobLauncher jbLauncher(JobRepository jobRepository) {
SimpleJobLauncher jobLauncher = new SimpleJobLauncher();
jobLauncher.setJobRepository(jobRepository);
return jobLauncher;
}
@Bean
public BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<Person> beanWrapperFieldSetMapper() {
BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<Person> fieldSetMapper = new BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<>();
fieldSetMapper.setPrototypeBeanName("person");
return fieldSetMapper;
}
@Bean
public FlatFileItemReader<Person> fileItemReader(BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper<Person> beanWrapperFieldSetMapper) {
FlatFileItemReader<Person> fileItemReader = new FlatFileItemReader<>();
fileItemReader.setResource(new ClassPathResource("person.csv"));
DelimitedLineTokenizer delimitedLineTokenizer = new DelimitedLineTokenizer();
delimitedLineTokenizer.setNames("id", "firstName", "lastName");
DefaultLineMapper<Person> defaultLineMapper = new DefaultLineMapper<>();
defaultLineMapper.setLineTokenizer(delimitedLineTokenizer);
defaultLineMapper.setFieldSetMapper(beanWrapperFieldSetMapper);
fileItemReader.setLineMapper(defaultLineMapper);
return fileItemReader;
}
@Bean
public JdbcBatchItemWriter<Person> jdbcBatchItemWriter(DataSource dataSource,
BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<Person> sqlParameterSourceProvider) {
JdbcBatchItemWriter<Person> jdbcBatchItemWriter = new JdbcBatchItemWriter<>();
jdbcBatchItemWriter.setDataSource(dataSource);
jdbcBatchItemWriter.setItemSqlParameterSourceProvider(sqlParameterSourceProvider);
jdbcBatchItemWriter.setSql("insert into person(id,firstName,lastName) values (:id, :firstName, :lastName)");
return jdbcBatchItemWriter;
}
@Bean
public BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<Person> beanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider() {
return new BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider<>();
}
@Bean
public Job jobCsvMysql(JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory, Step step) {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("jobCsvMysql").incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer()).flow(step).end().build();
}
@Bean
public Step step1(StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory, ResourcelessTransactionManager transactionManager,
ItemReader<Person> reader, ItemWriter<Person> writer, ItemProcessor<Person, Person> processor) {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1").transactionManager(transactionManager).<Person, Person>chunk(2)
.reader(reader).processor(processor).writer(writer).build();
}
}A default simple implementation of the Job interface is provided by Spring Batch in the form of the SimpleJob class which creates some standard functionality on top of Job, however the batch namespace abstracts away the need to instantiate it directly.
A Step is a domain object that encapsulates an independent, sequential phase of a batch job. Therefore, every Job is composed entirely of one or more steps. A Step contains all of the information necessary to define and control the actual batch processing.
ItemReader is an abstraction that represents the retrieval of input for a Step, one item at a time.
ItemWriter is an abstraction that represents the output of a Step, one batch or chunk of items at a time. Generally, an item writer has no knowledge of the input it will receive next, only the item that was passed in its current invocation.
ItemProcessor is an abstraction that represents the business processing of an item. While the ItemReader reads one item, and the ItemWriter writes them, the ItemProcessor provides access to transform or apply other business processing. If, while processing the item, it is determined that the item is not valid, returning null indicates that the item should not be written out.
TransactionManager – Spring’s that will be used to begin and commit transactions during processing.
Chunk – The number of items that will be processed before the transaction is committed.
JobRepository is the persistence mechanism. It provides CRUD operations for JobLauncher, Job and Step implementations. When a Job is first launched, a JobExecution is obtained from the repository, and during the course of execution StepExecution and JobExecution implementations are persisted by passing them to the repository.
JonLauncher represents a simple interface for launching a Job with a given set of JobParameters.
Spring Boot Main Class
Create below class for launching spring batch job. This class has a main method and @SpringBootApplication annotation.
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBatch.class, args);
}
}Testing Spring Batch CSV To MySQL
Run the main class, you will see the below output.
Processing: Person [id=1000, firstName=soumitra, lastName=roy]
Processing: Person [id=1001, firstName=souvik, lastName=sanyal]
Processing: Person [id=1002, firstName=arup, lastName=chatterjee]
Processing: Person [id=1003, firstName=suman, lastName=mukherjee]
Processing: Person [id=1004, firstName=debina, lastName=guha]
Processing: Person [id=1005, firstName=liton, lastName=sarkar]
Processing: Person [id=1006, firstName=debabrata, lastName=poddar]In the above output you see the job name, step name and also which row item from csv file is being processed. You also see the sql scripts have been executed and below tables have been created in the MySQL database with job details.
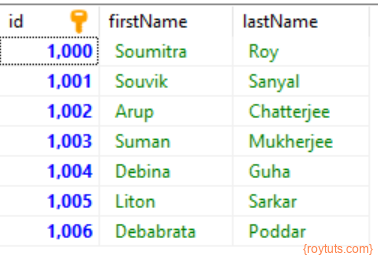
You will also see the person table has been populated with csv file data.
good post thanks for the information, but how can I do if my csv file is on an ftp server?